E-postformatfel
emailCannotEmpty
emailDoesExist
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
pwdLetterLimtTip
inconsistentPwd
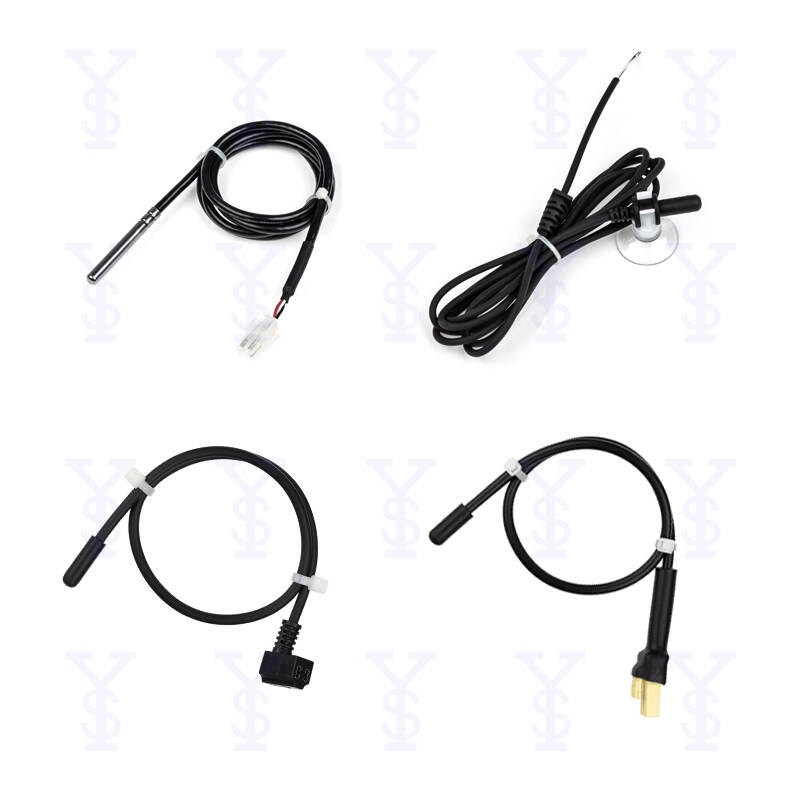


Understanding Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of machinery and industrial applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity is paramount. One of the critical components that plays a vital role in this aspect is the motor bearing temperature sensor. In this blog post, we will explore what motor bearing temperature sensors are, their importance, how they work, and their various applications. So, let's dive in and unravel the world of motor bearing temperature sensors.
What Are Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors?
Motor bearing temperature sensors are devices designed to monitor the temperature of bearings in electric motors and machinery. Bearings are essential components that facilitate smooth rotation and movement, reducing friction between moving parts. However, they are also susceptible to wear and tear, especially when operating under high loads or temperatures. By using temperature sensors, operators can monitor the condition of the bearings in real time, helping to prevent costly failures and downtime.
Why Are Temperature Sensors Important?
Preventing Overheating: One of the primary reasons for using motor bearing temperature sensors is to prevent overheating. When bearings exceed their optimal operating temperature, it can lead to lubricant breakdown, increased wear, and eventual failure. Monitoring the temperature allows for timely intervention.
Prolonging Equipment Life: Regular monitoring of bearing temperatures helps in maintaining the integrity of the bearings. By addressing issues early, companies can prolong the life of their machinery, which is essential for reducing operational costs and maximizing return on investment.
Improving Safety: Overheated motors can pose significant safety risks, including fire hazards and mechanical failures. By using motor bearing temperature sensors, operators can mitigate these risks and ensure a safer working environment.
Predictive Maintenance: With the data gathered from temperature sensors, companies can implement predictive maintenance strategies. This means that instead of waiting for a failure to occur, they can anticipate when maintenance is needed, minimizing unexpected downtime and repairs.
How Do Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors Work?
Motor bearing temperature sensors can operate through various technologies, including thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), and thermistors. Here's a brief overview of how these sensors work:
1. Thermocouples
Thermocouples are among the most common types of temperature sensors. They consist of two different metals joined at one end, creating a junction. When this junction is heated or cooled, it generates a voltage proportional to the temperature difference. The voltage can be measured and translated into a temperature reading.
2. RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors)
RTDs measure temperature by correlating the resistance of the sensor element with temperature changes. Typically made of pure platinum, the resistance of an RTD increases with temperature. This characteristic allows for precise temperature measurements, making RTDs highly accurate and stable.
3. Thermistors
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors that exhibit a significant change in resistance with temperature fluctuations. They are made from ceramic materials and are often used for applications requiring high sensitivity and precision. Thermistors can be categorized into two types: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient).
Installation and Placement of Sensors
For optimal performance, the placement and installation of motor bearing temperature sensors are crucial. Here are some guidelines:
Proximity to the Bearing: Sensors should be installed as close to the bearing surface as possible. This ensures accurate readings and quicker responses to temperature changes.
Avoiding External Interference: Ensure that the sensors are not influenced by external heat sources or environmental conditions, which could lead to false readings.
Proper Mounting: Sensors should be securely mounted to avoid vibrations, which could affect their accuracy and reliability.
Regular Calibration: Regularly calibrating the sensors ensures that they continue to provide accurate measurements over time.

Applications of Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors
Motor bearing temperature sensors find applications in various industries, enhancing performance and reliability. Here are some notable examples:
1. Manufacturing
In manufacturing facilities, motors are integral to machinery such as conveyors, pumps, and compressors. By using temperature sensors, manufacturers can monitor the bearings of these motors, ensuring they operate efficiently and reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
2. Renewable Energy
In wind turbines, bearings experience significant stress due to constant rotation and environmental factors. Implementing motor bearing temperature sensors allows for real-time monitoring, ensuring the longevity of turbine components and minimizing maintenance costs.
3. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, electric motors are increasingly used in various applications, from electric vehicles to industrial machinery. Monitoring motor bearing temperatures helps maintain the performance and reliability of these critical components.
4. HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely heavily on electric motors. By monitoring the temperatures of motor bearings in HVAC systems, operators can ensure optimal performance, preventing failures that could lead to costly repairs or system downtime.
Benefits of Using Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors
The integration of motor bearing temperature sensors offers several advantages for businesses:
Cost Savings: By preventing equipment failures and extending the life of machinery, companies can save significantly on repair and replacement costs.
Increased Efficiency: Monitoring temperature allows operators to optimize motor performance, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
Data-Driven Decisions: The data collected from temperature sensors enables operators to make informed decisions regarding maintenance schedules and operational adjustments.
Enhanced Reliability: With regular monitoring, businesses can ensure that their machinery operates reliably, reducing the risk of downtime and disruptions.
Challenges in Using Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors
While motor bearing temperature sensors offer numerous benefits, some challenges must be addressed:
Installation Costs: The initial cost of installing temperature sensors may be a concern for some businesses, particularly small operations. However, the long-term savings often outweigh the upfront investment.
Sensor Drift: Over time, sensors may experience drift, leading to inaccurate readings. Regular calibration and maintenance are essential to mitigate this issue.
Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating temperature sensors into existing monitoring systems can be complex. Companies need to ensure compatibility and may require technical expertise for seamless integration.
Future Trends in Motor Bearing Temperature Sensors
As technology continues to advance, so do motor bearing temperature sensors. Here are some emerging trends:
Wireless Technology: The development of wireless temperature sensors allows for easier installation and greater flexibility. These sensors can transmit data in real time, enabling remote monitoring.
Smart Sensors: The integration of smart technology allows sensors to analyze data and provide predictive maintenance insights, reducing the need for manual monitoring.
IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) enables temperature sensors to connect with other devices, creating a more comprehensive monitoring system. This connectivity allows for real-time data analysis and alerts.
Machine Learning: As machine learning technologies advance, sensors can analyze historical data to predict future failures, allowing for more proactive maintenance strategies.
Conclusion
Motor bearing temperature sensors are indispensable tools for ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of machinery across various industries. By providing critical data on bearing temperatures, these sensors help prevent costly failures, extend equipment life, and enhance overall safety. As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of motor bearing temperature sensors will expand, providing even greater benefits to businesses.
Investing in motor bearing temperature sensors is not just about preventing failures; it’s about fostering a culture of proactive maintenance and operational excellence. Whether in manufacturing, renewable energy, automotive, or HVAC systems, these sensors play a crucial role in driving efficiency and reliability in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape.
So, as you navigate the complexities of machinery maintenance, remember the significance of motor bearing temperature sensors. They are not merely components but vital allies in your quest for optimal performance and longevity in your operations.